BadRabbit Ransomware Removal Guide
Specialists at 411-spyware.com have reported about the discovery of a new ransomware-type infection. They have given it a name BadRabbit Ransomware. It has turned out that this new infection is very similar to a well-known ransomware infection Petya Ransomware in a sense that it also modifies the Windows Master Boot Record (MBR). Security specialists say that this infection primarily targets individual users and institutions (it has already affected Kiev’s Subway and Odessa’s Airport) in Eastern Europe; however, it has been noticed that it scans the network for vulnerable computers that could be infiltrated using Windows Server Message Block (SMB) too. Therefore, all computer users and institutions should take security measures no matter where they live/are based in. If you have already become one of the victims of this nasty infection, you should know that it is still possible to delete this ransomware infection from the system manually even though it is quite a sophisticated threat. The longer you keep it active on your system, the longer you could not use your computer normally, so we suggest that you take action today. You will not unlock your files by removing this threat from your computer, but you will definitely not allow it to affect your new files by disabling it.
Users usually infect their computers with BadRabbit Ransomware when they download fake Adobe Flash updates (install_flash_player.exe) and launch the “installer.” As has been observed, users might be taken to corrupted pages promoting these fake updates from legit news websites, which suggests that users must be cautious on all websites they visit. Once the malicious file downloaded from the web is launched, a new file infpub.dat is dropped straight to %WINDIR% and then the C:\Windows\system32\rundll32.exe C:\Windows\infpub.dat, #1 15 command is executed. Additionally, two more files (cscc.dat and dispci.exe) are created in the same directory (%WINDIR%). The cscc.dat file is a legit file. Specifically speaking, it is a legitimate driver used for malicious purposes. As for the other file dispci.exe, it is nothing more than the malicious executable. Both these files are used to encrypt victims’ personal files (e.g., .hdd, .java, .jpeg, .pptx, .psl, .vsdx, .xml, .zip, .sln, .sql, .tib, .der, .disk, .djvu, etc.) and modify the MBR.
Research has shown that BadRabbit Ransomware uses a strong encryption algorithm AES-128 to encrypt victims’ files. The AES key is also encrypted using RSA-2048. Needless to say, the ransomware infection has been programmed to do this not without reason. Cyber criminals behind this infection do not want users to be able to decrypt their files without the special decryptor. At the time of writing, its price was 0.05 BTC. The size of the ransom was indicated in the ransom note opened on the screen. BadRabbit Ransomware does not ask much money if compared to other sophisticated ransomware infections, but it does not mean that you should go to make a payment to cyber criminals. Our specialists say that paying money to malicious software developers is always a very risky activity because there are no guarantees that they will give the decryption tool to users after receiving their money. Unfortunately, there is nothing you could do to get your money back in such a case. Therefore, the only recommendation we have for those users who discover BadRabbit Ransomware on their computers is its complete removal. One of the steps you will need to take to remove this nasty infection is the MBR repair. Unfortunately, you could not decrypt your files if you do this, but, believe us, you need to fix it to be able to use your computer normally again.
Ransomware infections are sneaky threats, so we cannot promise that our advice will help you to prevent all of them from entering your system, but you should be very careful with software you download from the web because it might be malicious, especially if you download it from suspicious pages. Also, since ransomware infections are often spread via spam, you should stay away from all spam emails you get. Finally, enable an automated security application on your system to stay safe.
To use your PC normally again, you need to repair the MBR. You could do this only with your Windows installation DVD – it will allow you to boot into System Recovery Options. Once the MBR is fixed, go to delete three files belonging to this ransomware infection and the malicious file launched recently.
Delete BadRabbit Ransomware
Repair the Master Boot Record (MBR)
Windows XP
- Insert your disk of Windows XP.
- Boot from your CD.
- At Press any key to boot from CD…, press any key.
- At Welcome to Setup, press R.
- At Which Windows installation would you like to log onto, type 1 and tap Enter.
- When you see Type the Administrator password, enter the password and tap Enter.
- Insert fixmbr and if you see the question Are you sure you want to write a new MBR?, press Y and then tap Enter.
- Press Enter once again.
- Wait till the MBR is repaired.
- Remove the CD.
- Type exit and press Enter.
Windows Vista
- Boot from your Windows Vista CD/DVD.
- Choose your language/keyboard layout.
- At the Welcome screen, click Repair your computer.
- Select the operating system and then click Next.
- At System Recovery Options, click Command Prompt.
- Type these commends one after the other (press Enter after each commend): bootrec /FixMbr, bootrec /FixBoot, and bootrec /RebuildBcd .
- Wait till the MBR is fixed and remove CD/DVD.
- Type exit and tap Enter.
Windows 7
- Boot from your Windows 7 DVD.
- At Press any key to boot from CD or DVD…., press any key.
- Select a language and a keyboard layout.
- Click Next.
- Select the operating system and click Next (Use recovery tools that can help fix problems starting Windows must be checked).
- At System Recovery Options, click Command Prompt.
- Type bootrec /rebuildbcd, bootrec /fixmbr, bootrec /fixboot one after the other and tap Enter after each command.
- Remove the installation DVD.
Windows 8/8.1
- Boot from your Windows 8/8.1 installation DVD.
- At the Welcome screen, click Repair your computer at the bottom.
- Choose Troubleshoot and select Command Prompt.
- Type the bootrec /FixMbr, bootrec /FixBoot, bootrec /ScanOs, and bootrec /RebuildBcd commands one after the other and press Enter after each command.
- Remove the installation DVD from the tray.
- Type exit and press Enter.
- Reboot your PC.
Windows 10
- Boot from the installation DVD.
- Click Repair your computer at the Welcome screen.
- Click Troubleshoot.
- Select Command Prompt.
- Type bootrec /FixMbr, bootrec /FixBoot, bootrec /ScanOs, and bootrec /RebuildBcd commands and hit Enter after each of them.
- Remove the DVD.
- Type exit and press Enter.
- Restart your computer.
Remove the ransomware infection
- Open Explorer (press Win+E).
- Go to %WINDIR% (type the directory in the address bar at the top and press Enter to open it).
- Delete infpub.dat, cscc.dat, and dispci.exe.
- Remove the malicious file launched recently.
- Empty Recycle bin.
BadRabbit Ransomware Screenshots:
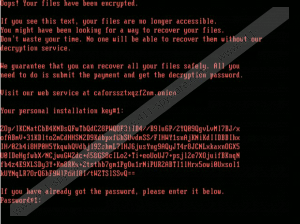
BadRabbit Ransomware technical info for manual removal:
Files Modified/Created on the system:
| # | File Name | File Size (Bytes) | File Hash |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | install_flash_player.exe | 441899 bytes | MD5: fbbdc39af1139aebba4da004475e8839 |
| 2 | infpub.dat | 410760 bytes | MD5: 1d724f95c61f1055f0d02c2154bbccd3 |
| 3 | cscc.dat | 210632 bytes | MD5: edb72f4a46c39452d1a5414f7d26454a |
| 4 | dispci.exe | 142848 bytes | MD5: b14d8faf7f0cbcfad051cefe5f39645f |
Memory Processes Created:
| # | Process Name | Process Filename | Main module size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | install_flash_player.exe | install_flash_player.exe | 441899 bytes |
| 2 | dispci.exe | dispci.exe | 142848 bytes |

